
10 J/kg 5000 J/kg
Mon 12/34/56 4:00
PARTICLE MATTER SIZED 1,0 µG/M3 AT SURFACE LEVEL
0,00 0,10 0,50 1,00 25,00 100,00 300,00 >500,00

SATELLITE DATA SOURCE
CAMS
Copernicus
EC + ECMWF
LIFE TIME
In general, the smaller and lighter a particle is, the longer it will stay in the air. Larger particles (greater than 10 micrometers in diameter) tend to settle to the ground by gravity in a matter of hours. The the smallest particles (less than 1 micrometer) can stay in the atmosphere for weeks and are mostly removed by precipitation.
THREAT TO HUMAN HEALTH
The effects of inhaling particulate matter has been widely studied in humans and animals and is associated with asthma, lung cancer, respiratory diseases, cardiovascular disease, premature delivery, birth defects, low birth weight and premature death.
Particulate matter smaller than 10 micrometers is to settle in the bronchi and lungs, and cause health problems. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) penetrates into the gas exchange regions of the lungs. The and very small particles (ultra fine particulate matter, PM0.1) passes through the lungs and affect other organs
THREATH TO ENVIRONMENT
Particle Matter affects both short and longwave radiation to produce a net negative radiative forcing.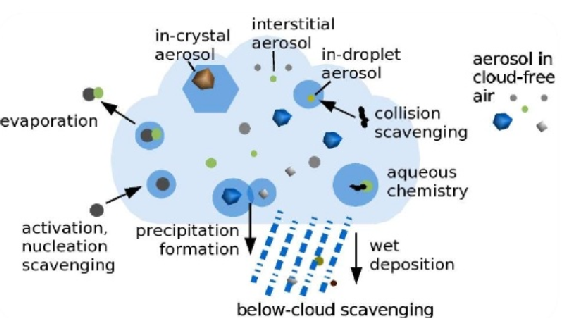
The Indirect effect consists of any change to the earth's radiative budget due to the modification of clouds in their cloud condensation nuclei.
DIMMING 6% !
India and China are dimmer at the surface today by at least 6 percent compared with their state in preindustrial times. The presence of two types of aerosols in the air reduces the amount of solar radiation reaching the surface of the Earth
Black carbon and organic carbon
Aerosols in brown clouds are made up primarily of black carbon and organic carbon. These aerosols, especially the black carbon component, absorb solar radiation, and this absorption results in enhanced solar heating of the atmosphere.
Sulfates and nitrates
Other aerosols, such as sulfates and nitrates, scatter solar radiation back to space.
Combined together both aerosols are r
- reducing in the amount of solar radiation reaching the surface
- Causing to lower surface temperatures.
- A lower surface temperature slows the rate of evaporation.
- Which reduces the amount of precipitable water in the atmosphere.
- The resulting declines in precipitation influences the regional hydrological cycle.
For example, atmospheric brown clouds have played a major role in decreases in summer monsoon rainfall in India since 1930. In addition, aerosol pollution has been linked to the southward shift of the summer monsoon in eastern China and to changes in precipitation patterns in other tropical regions.
LESS AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTION
Changes in precipitation and climate due to atmospheric brown clouds can modify regional agricultural production. These impacts are complex and are likely to be different depending on crop types. One study estimated that from 1985 to 1998 Indian rice output was reduced by 6.2 million metric tons (about 6.8 million tons—that is, enough rice to feed 72 million people) because of air pollution related to the Asian brown cloud.t
NOMENCLATURE EARTH NULSCHOOL
Wind: Wind speed at specified height
Temp: temperature at specified height
RH: relative humidity at specified height
WPD: Instantaneous Wind Power Density [measure of power available in the wind]
TPW: Total Precipitable Water [total amount of water in a column of air stretching from ground to space]
TCW: Total Cloud Water [total amount of water in clouds in a column of air from ground to space]
3HPA: 3-
CAPE: Convective Available Potential Energy from Surface [indicates the buoyancy of air, a measure of atmospheric instability and predictor of severe weather]
MSLP: Mean Sea Level Pressure [air pressure reduced to sea level]
MI: Misery Index [perceived air temperature as combination of heat index and wind chill]
SST: Sea Surface Temperature [temperature of the ocean surface]
SSTA: Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly [difference in ocean temperature from daily average during years 1981-
HTSGW: Significant Wave Height [roughly equal to mean wave height as estimated by a "trained observer"]
Cosc: Carbon Monoxide Surface Concentration [the fraction of carbon monoxide present in air at the earth's surface]
CO2sc: Carbon Dioxide Surface Concentration [the fraction of carbon dioxide present in air at the earth's surface]
SO2sm: Sulfur Dioxide Surface Mass [amount of sulfur dioxide in the air near the earth's surface]
DUex Dust Extinction [the aerosol optical thickness (AOT) of light at 550 nm due to dust]
SO4ex; Sulfate Extinction [the aerosol optical thickness (AOT) of light at 550 nm due to sulfate]
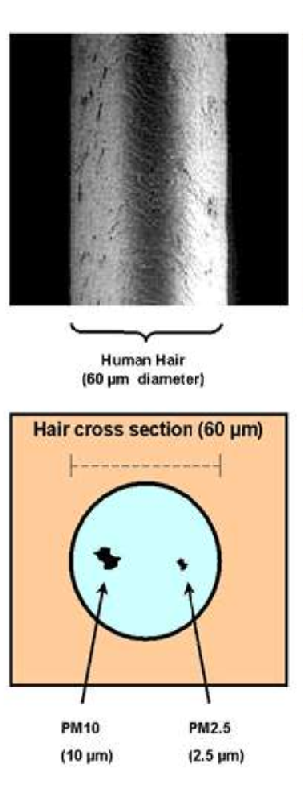
PM1: Particulate Matter < 1 µm [mass of atmospheric particles with a diameter less than 1 micron]
PM2.5 Particulate Matter < 2.5 µm [mass of atmospheric particles with a diameter less than 2.5 microns]
PM10: Particulate Matter < 10 µm [mass of atmospheric particles with a diameter less than 10 microns]
I NVERSION LAYERS
NVERSION LAYERS
Blankets of air trapping various sorts of air pollutants. Natural ventilation by the convection mechanism is not possible.
URBAN HEAT ISLAND
BROWN CLOUD
 RAMIFICATIONS INVERSION LAYERS
RAMIFICATIONS INVERSION LAYERS