CLIMATE CHANGE : THE MAGNITUDE OF THE PROBLEM
It began with the science that first identified climate change as a problem to human social, political and economic systems.
In its Fifth Assessment Report, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, a group of 1,300 independent scientific experts from countries all over the world under the auspices of the United Nations, concluded there's a more than 95 percent probability that human activities over the past 50 years have warmed our planet.
The ever-mounting evidence that Climate Change and its cascading impacts will become one of the greatest crises ever to face humanity.
Our planet itself will do well; it has been through far bigger changes. But will we?

GLOBAL TEMPERATURE RISE
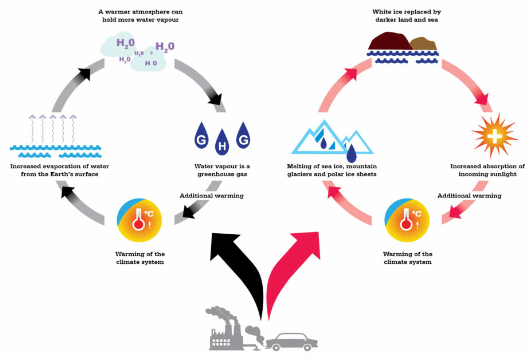
The average surface temperature of our planet has risen about 1,4 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century. A change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide and other human-made emissions into the atmosphere.
Most of this warming occurred in the past 35 years with several record warmest years since 2010.
 Global warming is a long-term rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system.
Global warming is a long-term rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system.
Climate change will effect humankind and its social-political structure in a negative way.
Human settlement, shortages of food and drinking water, in sight of an ever increasing world population, will become problematic in the nearby future.

WARMING OCEANS
“Oceans are the kitchens where our weather is prepared”.
Since first measurements in 1969 the top 700 meter warmed up approximate 0,5 degrees Celsius.
 “Our weather is influenced by the increased heat and water-vapour exchange with the atmosphere.
“Our weather is influenced by the increased heat and water-vapour exchange with the atmosphere.
Over 90% of the excess heat trapped by greenhouse gases has been stored in the oceans.
The world's oceans cover 71% of the earth surface and are about 4 km deep on average.
This represents a tremendous reservoir of heat.

EXTREME WEATHER EVENTS
The number of record temperature events and extreme weather phenomena is increasing.
Rising temperatures and air pollution are intimately connected in both directions.
 Higher temperatures are worsening storms, heat waves, floods, and droughts.
Higher temperatures are worsening storms, heat waves, floods, and droughts.
As our warming atmosphere holds more water vapour the weather phenomena become more intense.
Resulting in a increasing number of droughts, intense storms, and floods, that poses risks to public health, food production and overall our future.
Rising temperatures and air pollution are intimately connected in both directions. Urban Heat Islands arise combined with smog an soot made up of combustion gases, tiny particles of chemicals, soil, smoke, dust, or allergens. A
The Atmospheric brown cloud, a layer of air pollution containing aerosols such as soot or dust that absorb as well as scatter incoming solar radiation, and posing risks to human health and food security.

GLACIAL RETREAT
Glaciers are retreating almost everywhere around the world.
 Glaciers act as natural reservoirs of fresh water.
Glaciers act as natural reservoirs of fresh water.
Glaciers are a natural resource, and people all over the world use the meltwater that glaciers produce. Storing water in the winter and doling it out in the summer as the ice slowly melts.
A significant part of river flow comes from melting glaciers and provide water during dry spells .

OCEAN ACIDIFICATION: THE OTHER CARBON DIOXIDE PROBLEM
The acidity of surface ocean waters has increased by about 26 percent as result of humans emitting more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and hence more being absorbed into the oceans.
Threatening marine life such as Plankton being an important part of the marine food web.
 Acidification In time it could fundamentally altering marine food sources.
Acidification In time it could fundamentally altering marine food sources.
The Increasing acidity is causing coral bleaching and will have a range of potentially harmful consequences for marine organisms.
The estimated absorption of CO2 lowered the oceanic pH by around 0.1 to a level of 8.1.
The pH scale being logarithmic: the change in pH of 0.1 pH units since 1750 translates into an increase in of acidity of 26%.
Recent projections of oceanic pH indicated 7.7 by the end of this century.

SHRINKING ICE SHEETS
Artic and Antarctic ice sheets have decreased in mass.
The rate of Antarctica ice mass loss has tripled in the last decade.
 The loss of Artic and Antarctic ice sheets is of particular concern.
The loss of Artic and Antarctic ice sheets is of particular concern.
The white ice sheet surfaces decrease in area and less solar energy is reflected into space.
The surface and ocean water will warm up even more.
Global sea level rose nearly double in comparison with the last century and is accelerating slightly every year.













 Global warming is a long-
Global warming is a long- “Our weather is influenced by the increased
“Our weather is influenced by the increased  Higher temperatures are worsening storms, heat waves, floods, and droughts.
Higher temperatures are worsening storms, heat waves, floods, and droughts.  Glaciers act as natural reservoirs of fresh water.
Glaciers act as natural reservoirs of fresh water. Acidification
Acidification  The loss of Artic and Antarctic ice sheets is of particular concern.
The loss of Artic and Antarctic ice sheets is of particular concern. CLIMATE CHANGE RECORDS 2018
CLIMATE CHANGE RECORDS 2018  GREEN HOUSE EFFECT CO2 sticks around
GREEN HOUSE EFFECT CO2 sticks around MORTALITY
MORTALITY ALBEDO AND REFLECTIVENESS
ALBEDO AND REFLECTIVENESS The global shortage of fresh water in the nearby future is eminent and has become already a social and human disaster. Periodical droughts in the main foods producing regions are causing severe economic and environmental impacts. There is a big shortfall between the amount of food we produce today and the amount needed to feed everyone in 2050. There will be nearly 10 billion people on Earth by 2050. Food production depends on the availability of water.
The global shortage of fresh water in the nearby future is eminent and has become already a social and human disaster. Periodical droughts in the main foods producing regions are causing severe economic and environmental impacts. There is a big shortfall between the amount of food we produce today and the amount needed to feed everyone in 2050. There will be nearly 10 billion people on Earth by 2050. Food production depends on the availability of water.  NO BASIC SANITATION
NO BASIC SANITATION