THE CHANGING OF EARTHS NATURAL GREENHOUSE
Human activities are changing the natural greenhouse. Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). This happens because the coal or oil burning process combines carbon with oxygen in the air to make CO2. Also responsible for higher levels of CO2 is the clearing of land for agriculture, industry.
CO2 STICKS AROUND
 CO2 remains in the atmosphere longer than the other major heat-trapping gases emitted as a result of human activities. It takes about a decade for methane (CH4) emissions to leave the atmosphere (it converts into CO2) and about a century for nitrous oxide (N2O).
CO2 remains in the atmosphere longer than the other major heat-trapping gases emitted as a result of human activities. It takes about a decade for methane (CH4) emissions to leave the atmosphere (it converts into CO2) and about a century for nitrous oxide (N2O).
After a pulse of CO2 is emitted into the atmosphere, 40% will remain in the atmosphere for 100 years and 20% will reside for 1000 years, while the final 10% will take 10,000 years to turn over. This literally means that the heat-trapping emissions we release today from our cars and power plants are setting the climate our children and grandchildren will inherit.
EARTHS GREENHOUSE EFFECT BECOMES TOO STRONG
- If the greenhouse effect is too strong, Earth gets warmer and warmer.
- Due to increasing concentrations greenhouses gases, which are generated by human activity, average surface temperatures have been steadily increasing.
Too much heat stays trapped in the atmosphere.
The surface temperature on our planet ought to be on average approximately 15 degrees Celsius.
A higher content of atmospheric greenhouse gases results in an increased absorption and reabsorbing cycle.
Greenhouse Gases
read more…
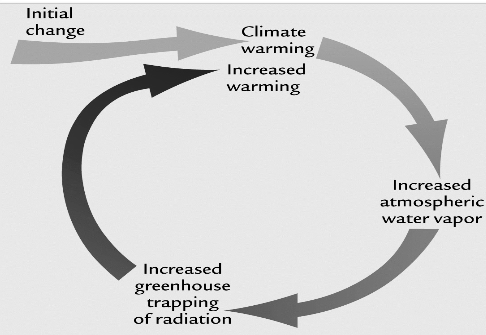
Fig. 1
A very simplified display of Earth’s Greenhouse effect becoming too strong.
More greenhouses gases results more absorbed heat in the atmosphere.
THE CHANGING OF EARTHS NATURAL GREENHOUSE
The disruption to Earth’s climate equilibrium has led to an increase in global average surface temperatures.


























 do what the roof of a greenhouse does. Trapping solar heat that is responsible for our weather as we know it.
do what the roof of a greenhouse does. Trapping solar heat that is responsible for our weather as we know it.

 THE
THE