THE IMPORTANCE OF ATMOSPHERIC CONVECTION
Convection within the troposphere is critical in order to prevent global warming
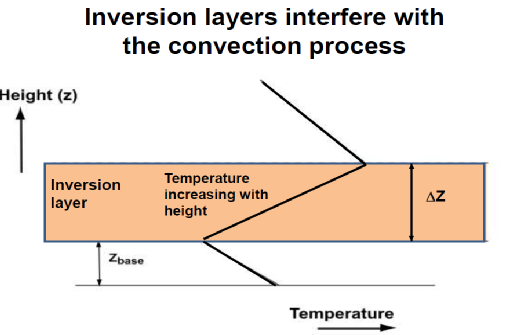
Convection is currently significantly inhibited by several atmospheric mechanisms such a :
SOLUTION PROVIDED BY AVE TECHNOLOGY
The Atmospheric Vortex Engine AVE can arguably help to overcome these inhibitory factors and in doing so yield:
RELATION OF CONVECTION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
Due to modest convection updraft velocities the temperature loss from the updraft
plume via radiation and mixing becomes too excessive which results in:
- An ineffective and incomplete convective heat transfer within the troposphere is forming low and midlevel clouds. The subsequent evaporation of these clouds increases atmospheric water vapour.
Note that water vapour is the planet’s most potent greenhouse gas
The high updraft efficiency typical of vortex flow leads to:
- High level reflective clouds.
- High precipitation efficiency, hence removal of water vapour from the atmosphere.
THE NEED FOR AN ATMOSPHERIC VORTEX ENGINE (AVE) : ‘FIRST AID’
The vortex engine is designed to initiate and optimise the convention mechanism.
In today’s time area it can serve as an first aid apparatus to mitigate the effect of climate change due to global warming. The phenomenon of global warming has a very great inertia. Just like an oil tanker, it reacts very slowly to steering movements. It is very difficult to determine the right course, given the enormous amount of interacting and entangled parameters and knowledge gaps that have to be filled up.
And at the same time has also bear in mind the challenges that we face:
To our opinion it is save to say that climate change will outrun - actually ”has outrun“ adaptation and mitigation strategies .
“ OCEANS ARE THE KITCHENS WHERE OUR WEATHER IS PREPARED”
OCEANS ARE THE KITCHENS WHERE OUR WEATHER IS PREPARED”
Our weather is influenced by the increased heat and water-vapour exchange with the atmosphere. Over 90% of the excess heat trapped by greenhouse gases has been stored in the oceans.
Read more…
THE IMPORTANCE OF ATMOSPHERIC CONVECTION
Dissipation of excess heat in the atmosphere and reducing airpollution.











 OCEANS ARE THE KITCHENS WHERE OUR WEATHER IS PREPARED”
OCEANS ARE THE KITCHENS WHERE OUR WEATHER IS PREPARED”